|
OPEN-CHANNEL HYDRAULICS: LECTURE 052 - UNIFORM FLOW FORMULAS
1. CHEZY FORMULA 1.01 The Chezy formula is:
Eq. 1
1.02 in which v = mean velocity, C = friction factor referred to as Chezy C, R = hydraulic radius, and S = energy slope. 1.03 The theoretical basis for the Chezy formula is the quadratic resistance law, which states that the bottom shear stress is proportional to the square of the velocity.
Eq. 2
1.04 in which ρ is the density of water, and f is a dimensionless friction factor.
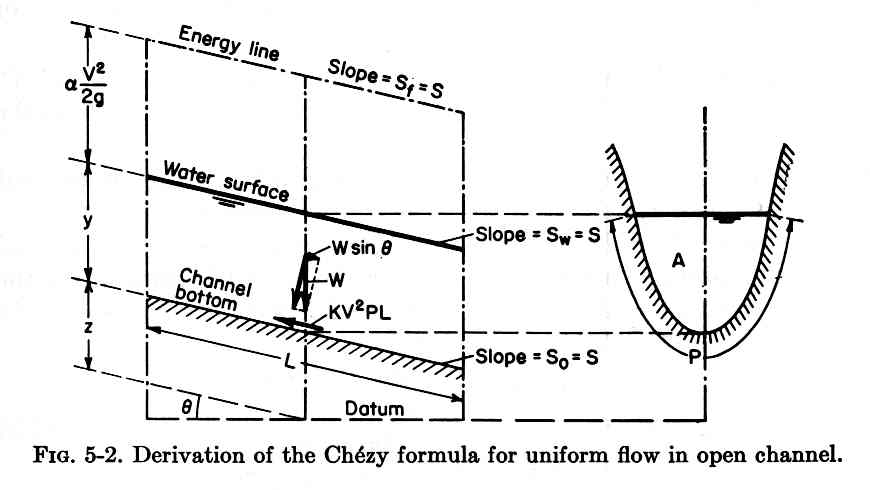
1.05 The frictional force along the wetted perimeter of the control volume is:
Eq. 3
Fig. 01
1.06 The gravitational force resolved along the direction of motion is:
Eq. 4
1.07 Assuming that sin θ can be approximated as tan θ, that is, a channel of small slope S:
Eq. 5
1.08 Equating gravitational and frictional forces:
Eq. 6
1.09 With hydraulic radius defined as area over the wetted perimeter:
Eq. 7
1.10 Solving for velocity:
Eq. 8
1.11 Therefore, Chezy C is:
Eq. 9
1.12 The dimensionless friction factor is:
Eq. 10
1.13 The energy slope is:
Eq. 11
1.14 For a hydraulically wide channel, for which hydraulic radius and hydraulic depth are nearly equal:
Eq. 12
1.15 Therefore, the dimensionless Chezy equation for hydraulically wide channels is:
Eq. 13 2. MANNING FORMULA 2.01 The Manning formula is:
Eq. 14 2.02 where n is the Manning's n, or Manning's friction coefficient. 2.03 This formula is in SI units. In U.S. Customary units:
Eq. 15 2.04 The constant 1.486 is equal to:
Eq. 16 2.05 To compare with Chezy, the Manning formula is expressed as:
Eq. 17 2.06 Therefore, Chezy C is:
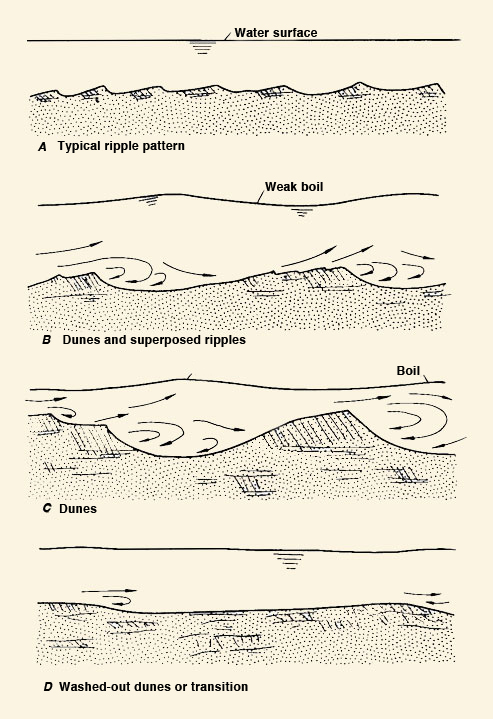
Eq. 18 2.07 This implies that while Chezy C may be a mild function of the hydraulic radius, Manning's n is a constant. 2.08 Manning's n may be a constant in prismatic artificial channels. However, Manning's n is not a constant in natural channels. 2.09 In natural channels, n varies with stage and discharge. 2.10 In natural sandbed streams, which are actively moving their beds, n varies as a function of the prevailing flow regime, either lower or upper regime. 2.11 Lower regime is characterized by ripples and dunes, with form friction predominating. Fig. 02
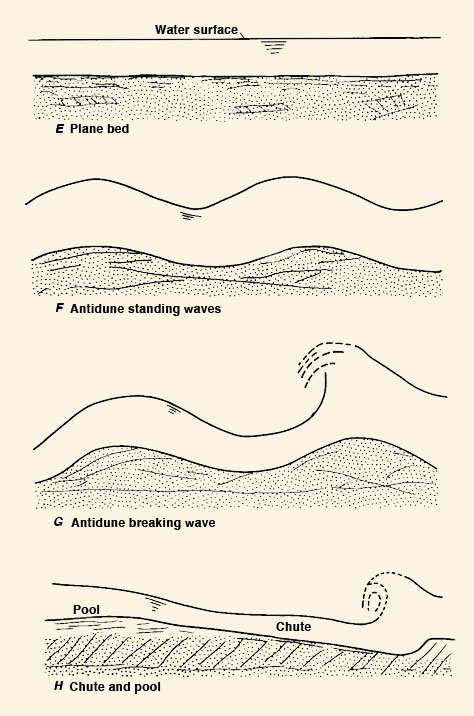
2.12 Under upper regime, ripples and dunes are obliterated, and grain friction predominates. Fig. 03
Fig. 01
Fig. 02
Fig. 03
Narrator: Victor M. Ponce
Music: Fernando Oñate
Editor: Flor Pérez
Copyright © 2011
Visualab Productions
All rights reserved
|